The textile platform is an innovation laboratory, open to textile industrials wishing to develop products that are offering an answer to demanding (product) criteria and to create commercial opportunities in technical textile niche markets (energy, aviation, medical devices).
In a globalized economy, Belgian and European textile producers have largely turned away from the two traditional sectors (being clothing and upholstery) and are focusing to very specific products for technical applications, requiring adapted processes, materials and knowledge.
High performance fibres including carbon and basalt fibres, glass fibres and natural fibres (flax or hemp) can be used for composite formation. The matrix to consolidate the composite can be both a thermoset or thermoplastic polymer, biobased or not.
Knitting
The Centexbel knitting machines are mainly used to for the production of very particular items, including smart/electronic textiles and knitted supports for composites or for medical and other high-tech purposes in the framework of R&D projects.
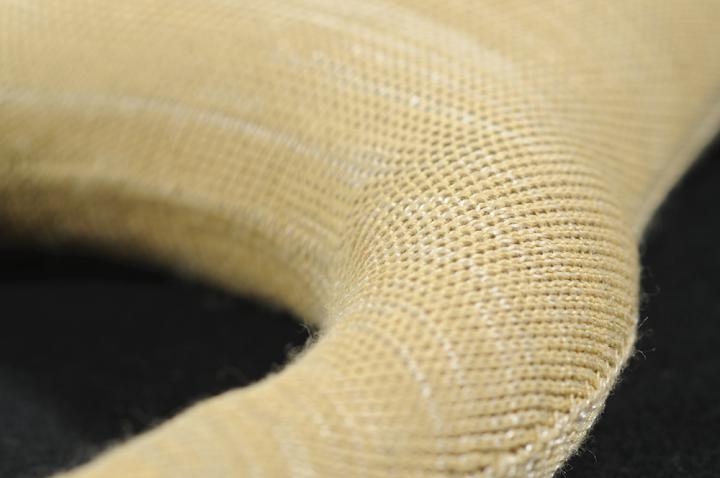

Knitted reinforcement for composites
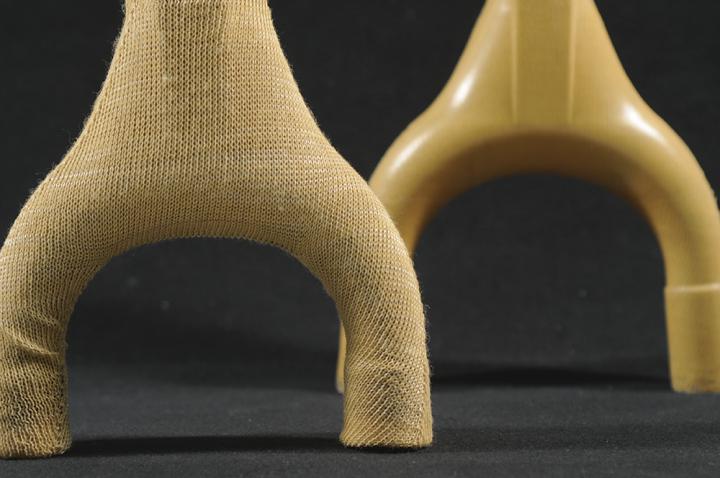

Composite reinforced with circular knitwear
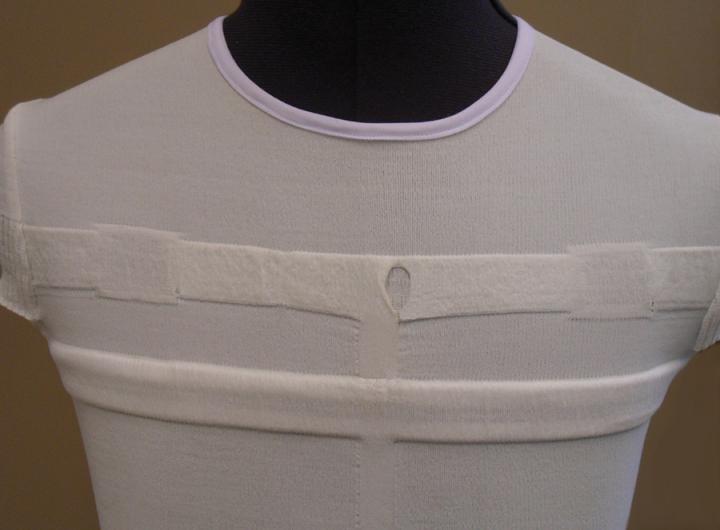

Smart shirt with knitted conductive fibres
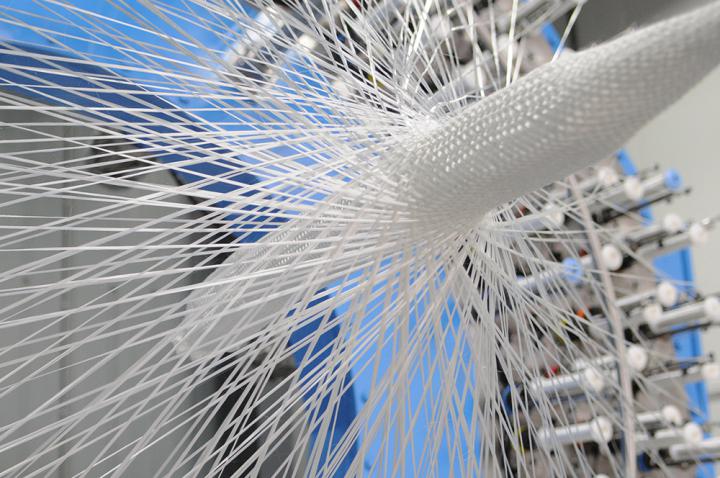
Braiding
Characteristics
- multilayer braiding: 4 interlocked layers, each made by means of 65 bobbins (256 in total)
- 3D braiding allowing complex shapes
- dimensions: 3640 x 3496 x 3640 mm
Suited for all technical fibres (carbon, glass, metal, polyethylene HD,…) applied in composites.
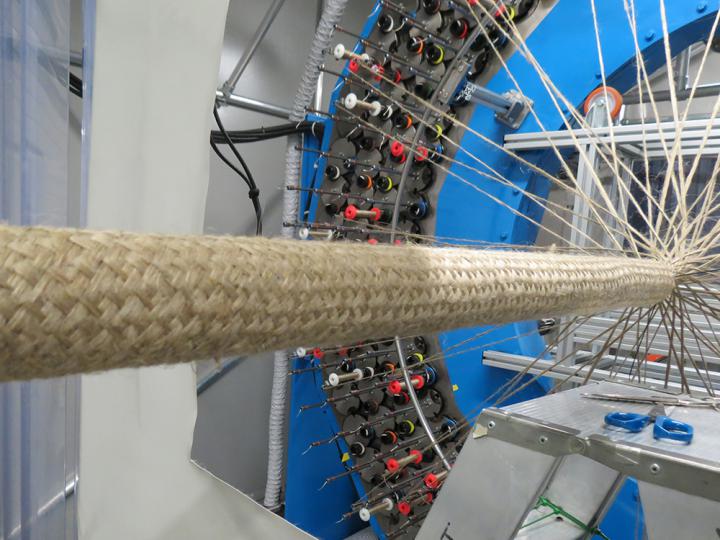
Large flax braid for high-end composites
3D Braiding for high-end composite applications
For the sake of weight reduction and high performance, fibre-reinforced composite materials are developed and widely applied in industries (e.g. aerospace, transportation and marine) as a supplement / replacement of metallic alloys.
Conventional laminated composite materials have accounted for major appliance in structural design due to the traits in specific stiffness, strength and fatigue performance. However, the fibrous discontinuity through thickness orientation reduces damage tolerance, which partially restrict its industrial appliance for some specific purposes. This stimulates the development of three-dimensional (3D) braided composites that can be manufactured economically and productively with well-designed textile procedures.
Due to the fibre distribution in thickness direction, inter-laminar failure (e.g. delamination), is dramatically eliminated. This reinforcement usually contributes to an improvement of damage tolerance and impact resistance.
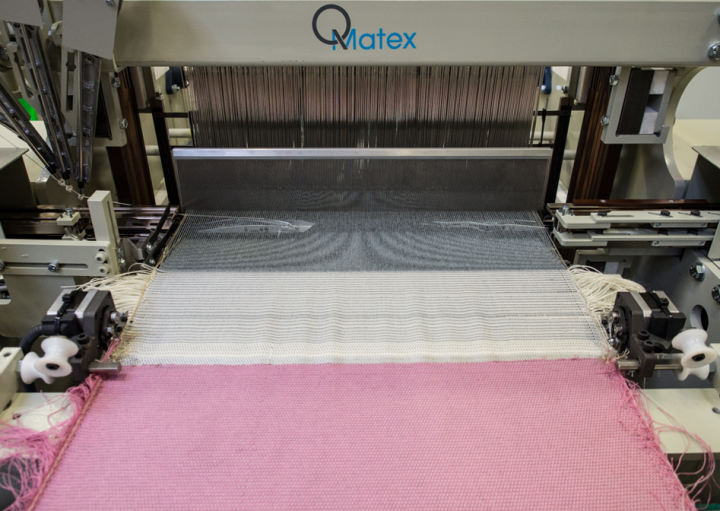
Weaving
2D & 3D weaving loom QS-4-500 Dobby
Technical textiles and complex multi-layered fabrics for composite reinforcements
- Development of novel, even lighter and more resistant 3D shaped composite reinforcement fabrics.
- This industrial machine is designed for the production of fabrics with a limited width that are suited to produce prototypes of new structures or to evaluate different materials.
- This weaving machine is also very interesting to industrials desiring to develop novel fabric structures or to experiment with new materials.
In the framework of the MACOBIO (FEDER) project, we explore the processing of natural and biobased fibres on this weaving machine. The reinforcements are being consolidated in a composite which performances are then characterised.
Characteristics:
- Working width: max 500 mm
- Double weft insertion system – Possibility to mount 4 insertion clamps
- Each frame is driven by a separate servo motor to obtain different positions and motion profiles
- Dobby system with shed opening to 300 mm
- 8 frames, extendable to 24
- Equiped with a parallel reed motion
- Yarn feed by either a set of two beams or through a bobbin creel with 500 postions
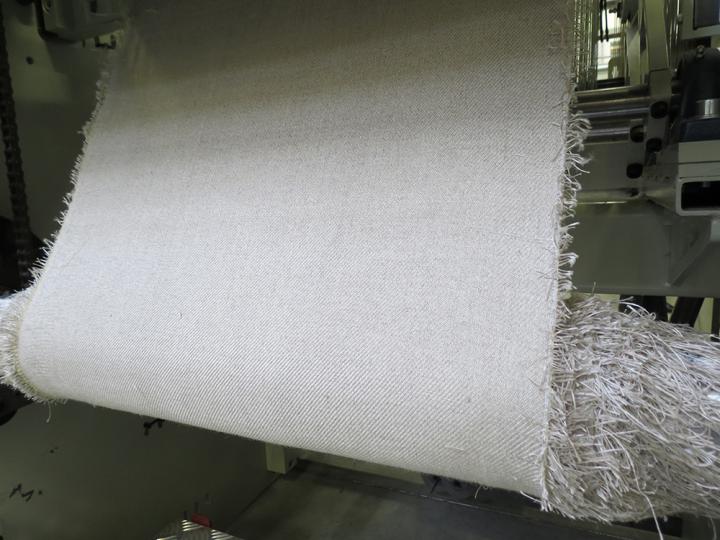

100% flax twill for composite formation (Macobio project)
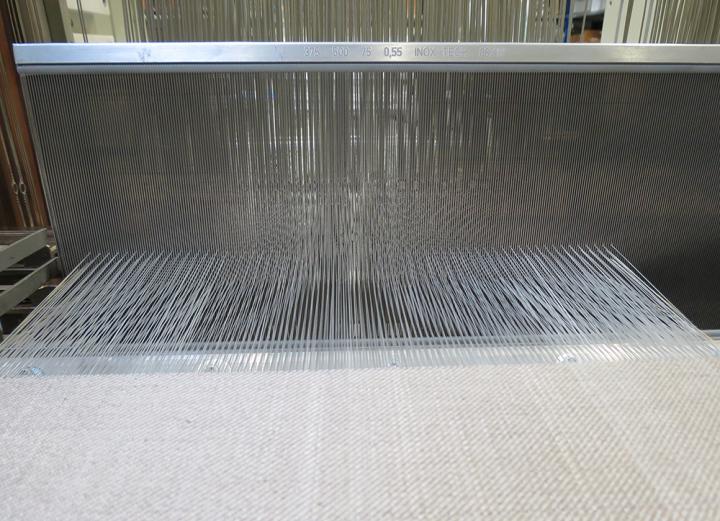

Hybrid weave flax/PLA for composite formation (Macobio project)
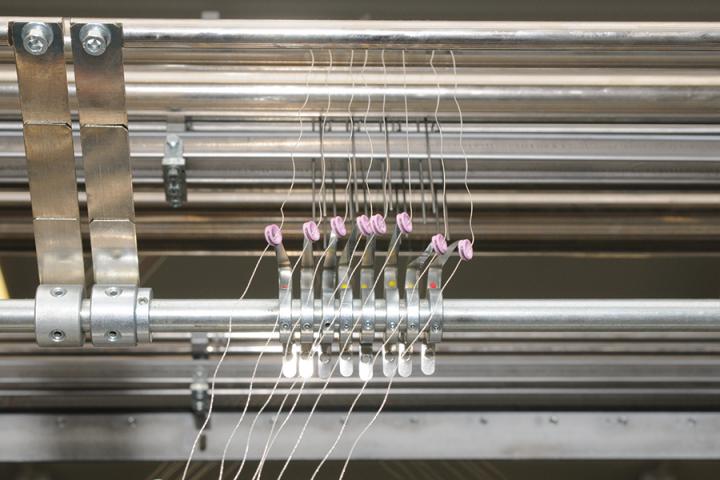
Embroidering
Mixed Head Embroidery Machine
The embroidery technique enables us to apply fibres in all directions to modify the properties of a composite reinforcements according to the requirements of the final application.
Embroidery process
- great freedom of design for special textile structures thanks to the applicatons of all sorts of yarns from all sorts of materials in all directions
- design of textile integrated sensors with almost unlimited shape variations
- design of complex reinforcing structures for composites
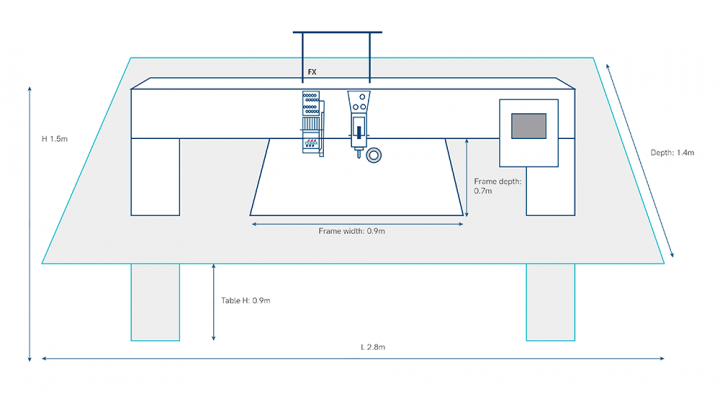
Mixed head embroidery machine - sketch
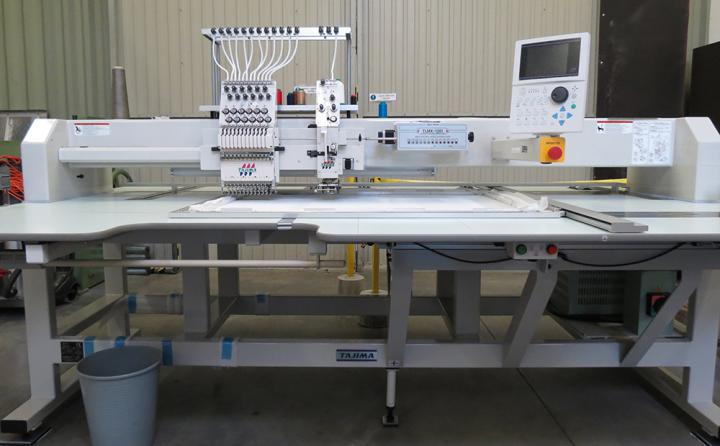

Embroidery machine is completing the Centexbel textile platform in Grâce-Hollogne
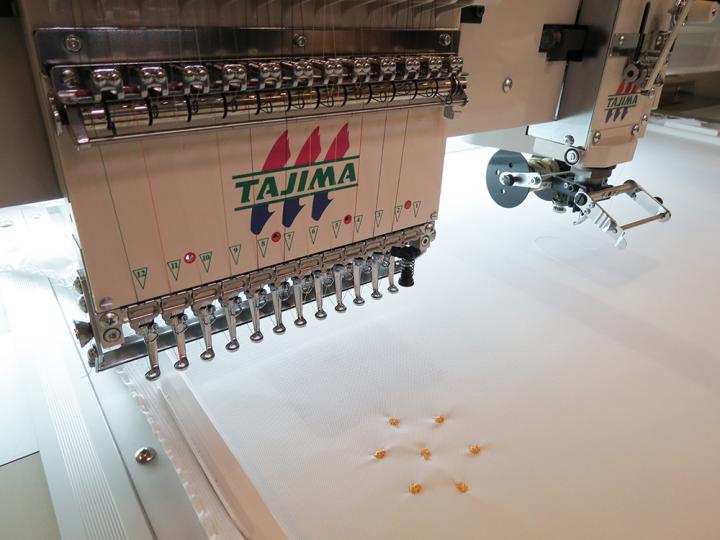

Detail of the embroidery heads